Nodes Browser
ComfyDeploy: How Wild Divide works in ComfyUI?
What is Wild Divide?
This extension provides the ability to build prompts using wildcards for each region of a split image.
How to install it in ComfyDeploy?
Head over to the machine page
- Click on the "Create a new machine" button
- Select the
Editbuild steps - Add a new step -> Custom Node
- Search for
Wild Divideand select it - Close the build step dialig and then click on the "Save" button to rebuild the machine
Wildcard Divide
ComfyUI custom node that specifies wildcard prompts for multiple regions
 The above workflow is docs/example.json.
The above workflow is docs/example.json.
Wildcard Divide Node
This node incorporates the syntax of Impact Pack Wildcards while introducing additional syntactical features.
Weighted Child Selection
You can assign selection weights to options by prefixing them with a numerical value. This number determines the likelihood of that particular option being chosen.
hair:
- 4, blonde
- 5, black
- 1, red
In this example, invoking __hair__ will result in "blonde" being selected with a probability of 4/(4+5+1) = 4/10 = 0.4.
When a numerical prefix is omitted, a default weight of 1 is assumed.
This weighted selection mechanism is functionally equivalent to the following syntax in Impact Pack Wildcards:
hair:
- {4::blonde|5::black|1::red}
Pattern-based Selection
Lines that start with / are pattern matchers. These are selected when the pattern matches
the previously generated prompt. Here's an example:
outfit:
- blouse, skirt, __legs__
- shirt, pants, __legs__
- swimsuit, __legs__
legs:
- /skirt/ stockings
- /pants/ socks
- bare feet
Here's how the pattern matching works:
-
When
__outfit__expands toblouse, skirt(1/3 probability):__legs__will only consider options matching/skirt/plus unmatched options- Therefore, it will randomly choose between
stockingsorbare feet
-
When
__outfit__expands toshirt, pants(1/3 probability):__legs__will only consider options matching/pants/plus unmatched options- Therefore, it will randomly choose between
socksorbare feet
-
When
__outfit__expands toswimsuit(1/3 probability):- Since no patterns match, only unmatched options are considered
- Therefore, it will select
bare feet
Note: Options without any pattern matcher (like bare feet in this example) are always included
as candidates, regardless of the previous prompt.
Pattern Alternatives
When a line includes !, the text after ! will be selected when the pattern does not match the prompt. For example:
outfit:
- blouse, skirt
- dress
- swimsuit
legs:
- /swimsuit/ bare feet ! stockings
In this example, stockings will be selected when the outfit doesn't contain swimsuit (i.e., when blouse, skirt or dress is selected). Conversely, if swimsuit is selected, bare feet will be chosen.
Exclusive Pattern Matching
When a pattern ends with =, it becomes an exclusive pattern that will remove all non-matching options from consideration. For example:
outfit:
- blouse, skirt
- dress
- swimsuit
legs:
- /skirt/= stockings
- bare feet
In this example:
-
When
__outfit__selectsblouse, skirt(1/3 probability):- The
/skirt/=pattern matches - Due to the
=suffix, all non-matching options (in this case,bare feet) are excluded - Therefore,
stockingswill be selected with 100% probability
- The
-
When
__outfit__selects eitherdressorswimsuit:- The
/skirt/=pattern doesn't match - Only the non-pattern option
bare feetremains available - Therefore,
bare feetwill be selected with 100% probability
- The
Pattern Matching with Conditional Exclusion
The =~ suffix creates a sophisticated pattern matching rule that combines conditional exclusion with fallback behavior. When a pattern ends with =~, it implements the following logic:
outfit:
- blouse, skirt
- dress
- swimsuit
legs:
- /skirt/=~ stockings
- bare feet
- socks
This operates in two distinct modes:
-
When Pattern Matches: If
__outfit__containsskirt(probability: 1/3):- The
/skirt/=~pattern activates - All non-matching options (
bare feet,socks) are excluded stockingsis selected with 100% probability
- The
-
When Pattern Fails: If "skirt" is not present in
__outfit__:- The pattern-matched option (
stockings) remains in the candidate pool - All options become eligible for selection
- Random selection occurs between
stockings,bare feet, andsocks
- The pattern-matched option (
This mechanism provides a elegant way to enforce specific combinations while maintaining flexibility when conditions aren't met.
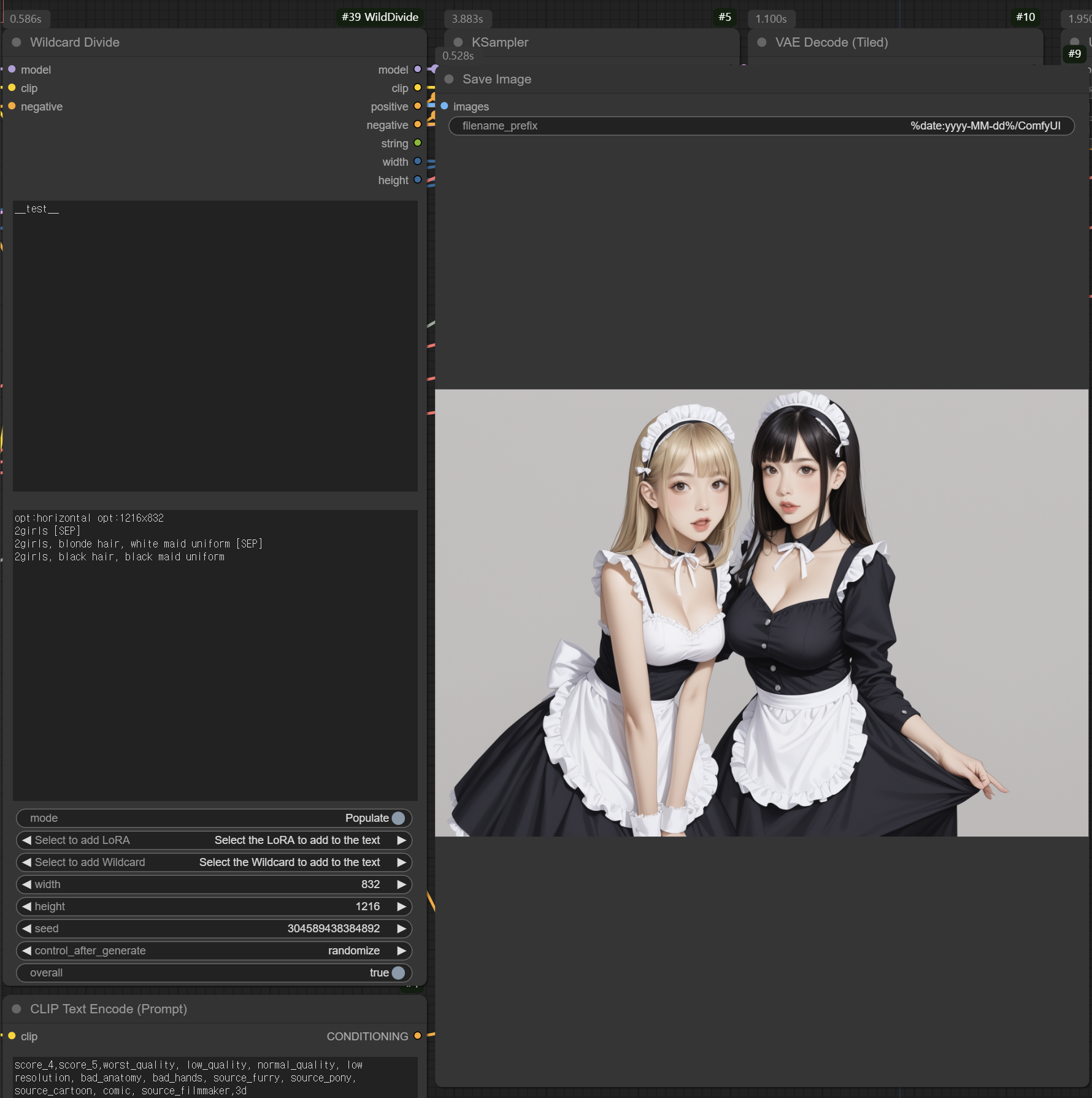
Split region
You can use [SEP] to divide an image into different regions. Each [SEP] divides the image into n equal parts.
scene: 2girls [SEP] blonde hair [SEP] black hair
For example, if written as above, 2girls would be applied to the entire image, blonde hair to the left half of the image, and black hair to the right half.
Split Direction
You can specify the orientation of the split using the opt:horizontal and opt:vertical options.
scene:
- opt:horizontal 2girls [SEP] blonde hair [SEP] black hair
- opt:vertical sky [SEP] blue sky [SEP] red sky
This syntax allows for precise control over image segmentation:
-
Horizontal Split (Left to Right): If the first option is selected, the image is divided horizontally. In this case:
2girlsapplies to the entire imageblonde hairis applied to the left halfblack hairis applied to the right half
-
Vertical Split (Top to Bottom): If the second option is chosen, the image is segmented vertically:
skyis applied across the entire imageblue skyaffects the top halfred skyinfluences the bottom half
Image Size Specification
You can define the dimensions of the output image using the opt:widthxheight syntax. This feature allows for dynamic image size adjustment based on the selected option.
scene:
- opt:1216x832 2girls [SEP] blonde hair [SEP] black hair
- opt:832x1216 sky [SEP] blue sky [SEP] red sky
In this example, selecting the second option would result in an image with dimensions of 832x1216 pixels.
To implement this functionality, ensure that you connect the width and height outputs to the empty latent image node in your workflow. This connection enables the dynamic resizing of the output based on the specified dimensions.